Search

Researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia have been awarded more than $11 million to support vital child health projects, under the Federal Government’s Medical Research Future Fund.

Congratulations to Associate Professor Asha Bowen, who has been awarded the 2022 Frank Fenner Award for Advanced Research in Infectious Diseases.

Prof Jonathan Carapetis has been elected as a new Fellow of the prestigious Australian Academy of Science in recognition of his pioneering, paradigm-shifting expertise in infectious diseases.

Rheumatic heart disease, a deadly yet entirely preventable heart disease taking the lives of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people, is finally on the verge of elimination thanks to new research

Once you hear it, you won’t be able to get it out of your head – and that’s exactly the point of the new song ‘Boom Boom’.
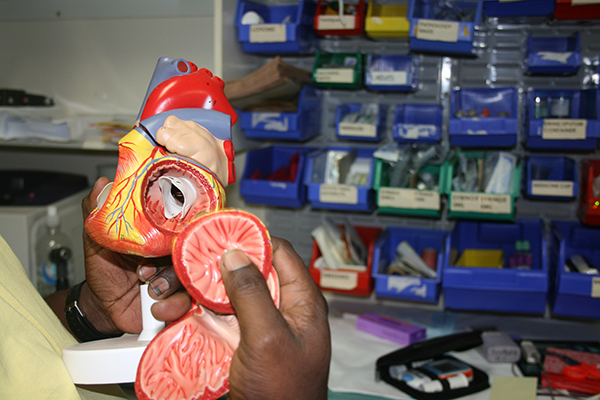
Health activities driven by remote Indigenous communities may be key to the sustainable and successful treatment and prevention of a potentially fatal disease, a study has found.
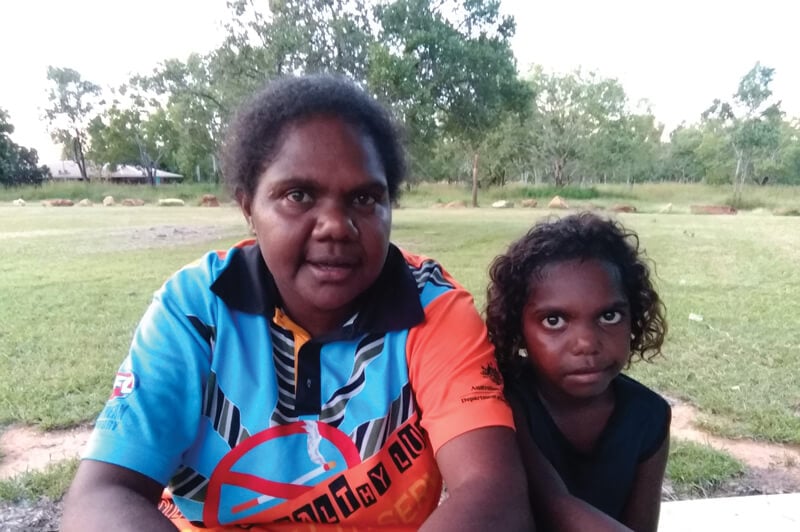

Collaboration is the driving force behind ‘END RHD Demonstration Communities’ – a new community-driven, research-backed approach to tackling rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in remote Australia.

The Kids Research Institute Australia and Menzies School of Health Research have joined forces with Danila Dilba Health Service to look at improving treatment for RHD.

A new report predicts rheumatic heart disease (RHD) will lead to over 500 preventable deaths and cost the Australian health system $317 million by 2031 if no further action to tackle the disease is taken.

The Kids Research Institute Australia & Menzies School of Health Research will lead an international project to develop a diagnostic tool for acute rheumatic fever.
