Search
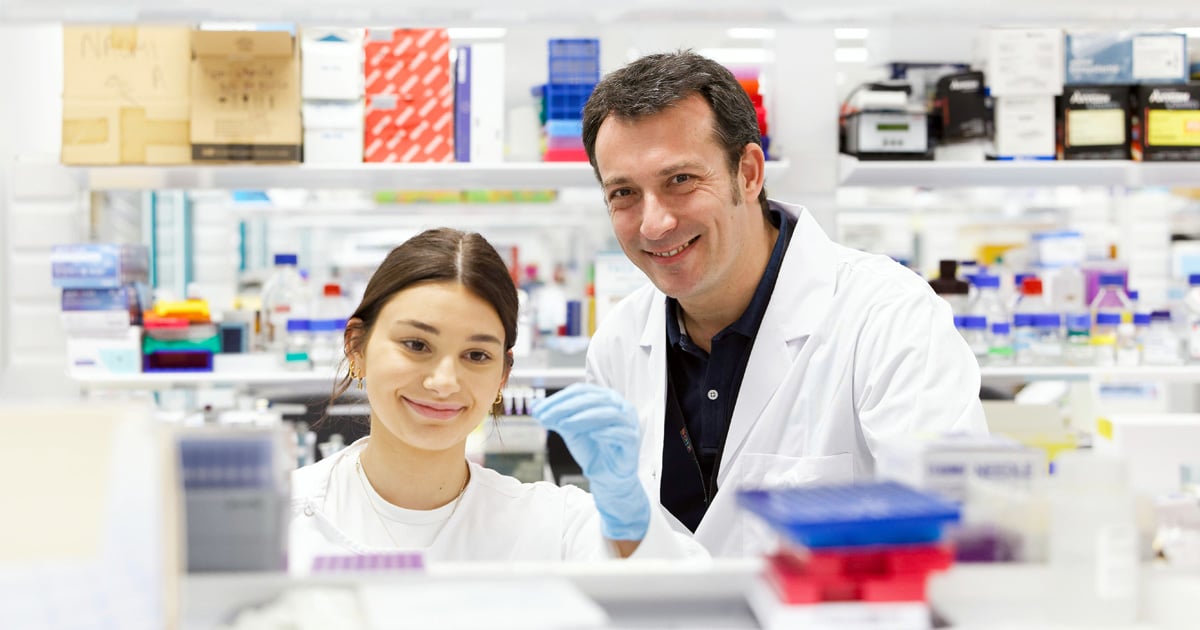

A team of world-leading scientists has secured $5 million in funding from the Leukaemia and Lymphoma Society to advance the fight against leukaemia in children with Down syndrome.

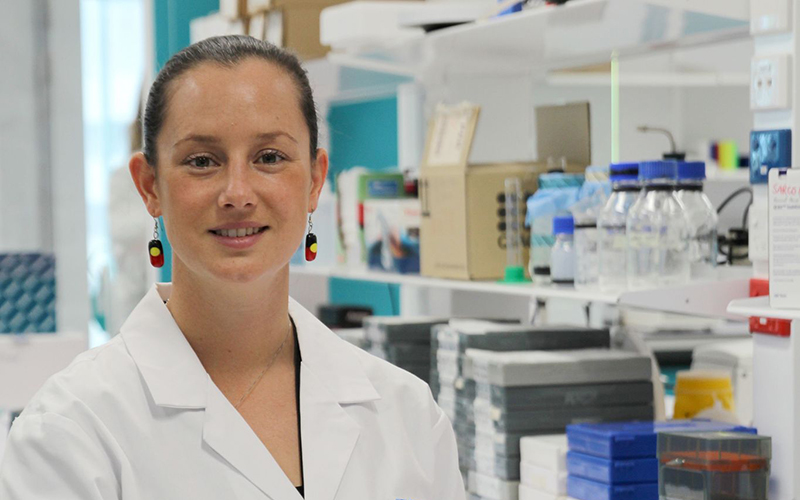
One of the researchers who helped crack the code of 10-year-old Northam girl Charlotte Patterson’s incredibly rare disease has received State Government funding that will allow her to use the same methods to rapidly assess the cases of hundreds more patients living with undiagnosed disease.

The Kids Research Institute Australia brain cancer researcher, Dr Jessica Buck will today join the ranks of a select group of brilliant female scientists.
In the field of cancer research, lobbying efforts by the The Kids Cancer Centre have contributed to major initiatives including Australia’s first personalised medicine program for children with high-risk cancer, and a mission to boost survival rates in brain cancer patients.

Michelle Pianta knew deep down something was very wrong with her seven-and-a-half month old son Jackson as she waited at Bunbury Hospital for his blood results.

Dr Rishi Kotecha knows too well the devastation of a leukaemia diagnosis in a child, treating children as a consultant at Princess Margaret Hospital.

In an exciting breakthrough for cancer treatment, a new weapon to enable the immune system to combat the disease may have been unlocked.

A The Kids Research Institute Australia researcher will investigate new ways to harness the body’s own immune system to fight melanoma, thanks to Cancer Council WA funding.

Dr Nick Gottardo and Dr Raelene Endersby from The Kids Research Institute Australia are the driving force behind an innovative, global action group on child brain cancer.
The goal of Project Children's Cancer is to discover new therapies that are more effective and less toxic to fight aggressive cancers in babies and children.
