Search

Researchers at The Kids Research Institute Australia have found children with vitamin D deficiency are more likely to develop asthma.

Join us for our Annual Community Lecture entitled "You Are What You Breathe" with Professor Stephen Holgate.
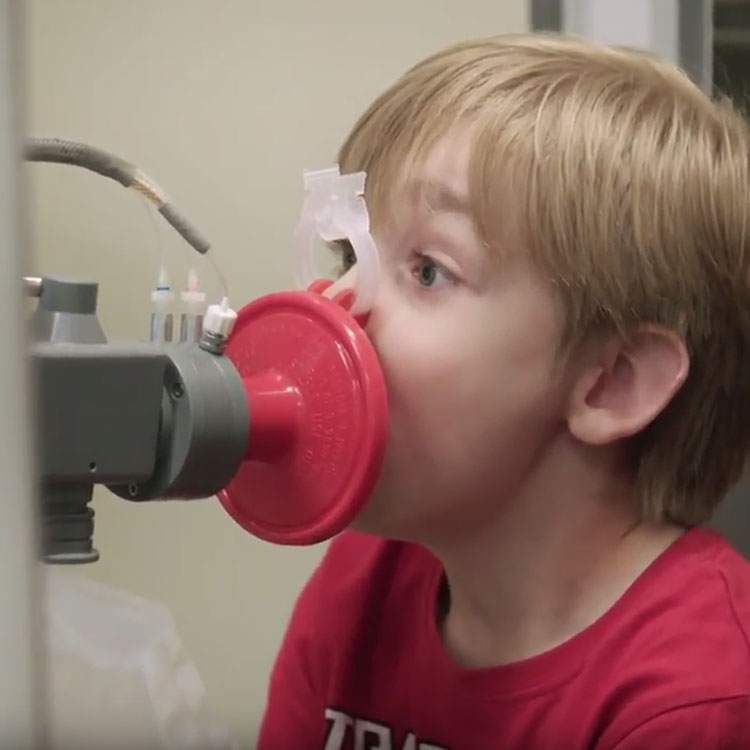
Australia has one of the highest burdens of asthma in the world. In this video, two Perth families share their story of raising children with the respiratory co
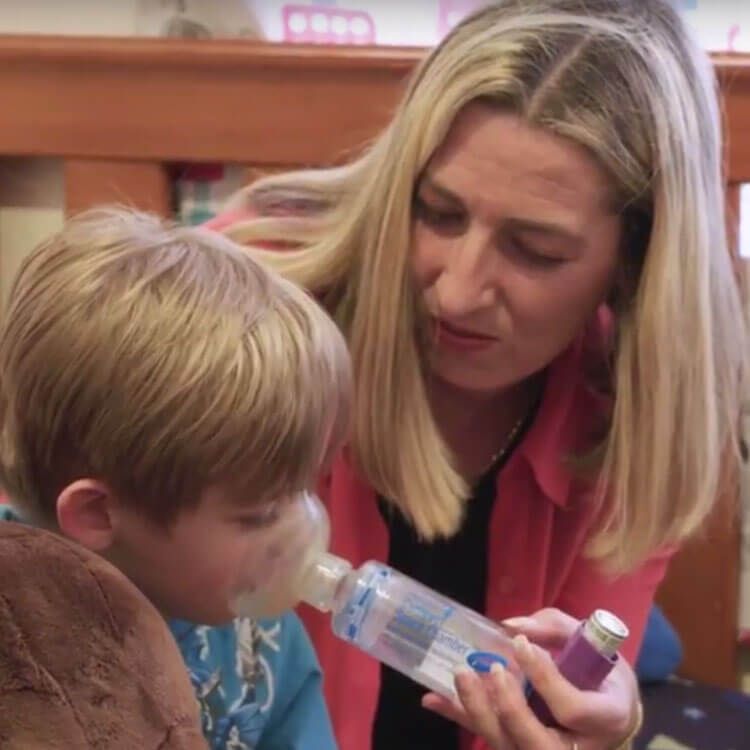

Michelle has spent countless nights watching her son struggle to breathe. Our researchers are working to find better treatments for kids living with asthma.
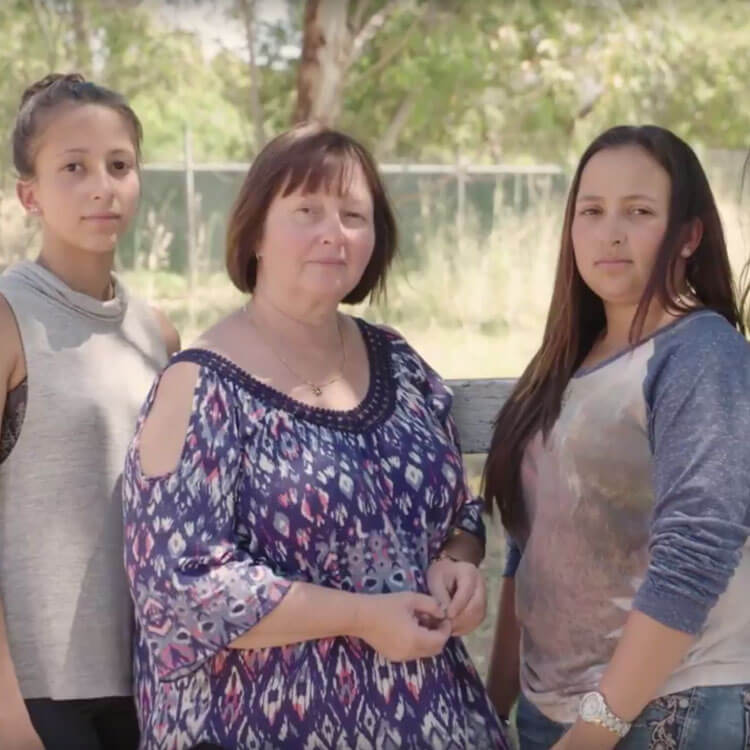
The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers are at the forefront of asthma research globally. Watch Karen's story to learn why it's so important.
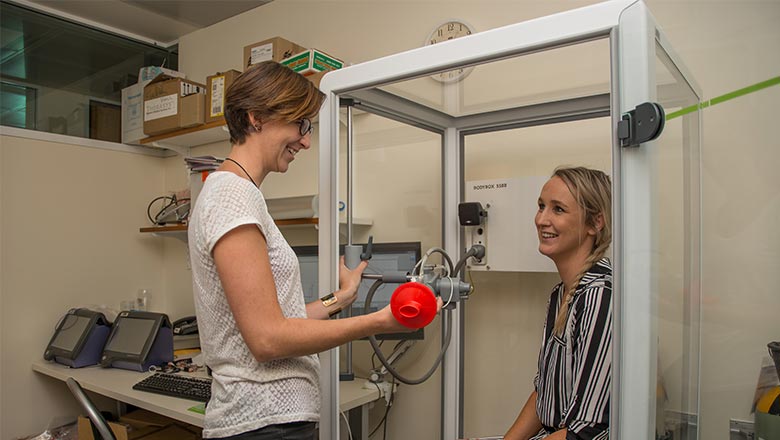

Researchers are urging caution in the use of a widely accepted test for diagnosing asthma, after their study found it may not be accurate in some settings.
Improving health outcomes for pregnant women with allergic asthma and their babies: Thursday 22nd May.
New research aimed at reducing the airway damage caused by asthma attacks in children has just begun at The Kids for Child Health Research in WA.
Professor Graham Hall is leading a study looking at exercise-related asthma in young children, and we need volunteers to take part.
Telethon Institute for Child Health Research scientist Dr Anthony Bosco has been recognised for his cutting edge research investigating asthma attacks
