Search

News & Events
“Natural killer” donor cells fighting kids leukaemiaNew research by The Kids shows donor immune cells are highly effective at boosting the body’s response against leukaemia.

News & Events
Child health research set to benefit from national grantsResearchers at The Kids Research Institute Australia have been awarded $4.6 million in national funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) and Medical Research Future Fund (MRFF) to help support child health research.

News & Events
Cancer researcher to use Forrest Fellowship to tackle high rates of relapse after sarcoma surgeryA The Kids Research Institute Australia researcher aiming to reduce the high rate of relapse in children after cancer surgery has won a prestigious post-doctoral fellowship from the Forrest Foundation.

News & Events
WA Child Research Fund grants boost research for premmies, kids with cancer and rare diseasesThe Kids Research Institute Australia researchers have been awarded 12 of 16 grants under the latest round of funding from the WA Child Research Fund

News & Events
Pioneering research could be key to keeping cancer in checkCancer research is being reimagined after a collaboration between The Kids Research Institute Australia, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity.
News & Events
Researchers identify immune cell that puts cancer to sleepA team of Australian scientists including cancer researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia have made a crucial breakthrough in understanding how the immune system puts cancer to sleep.
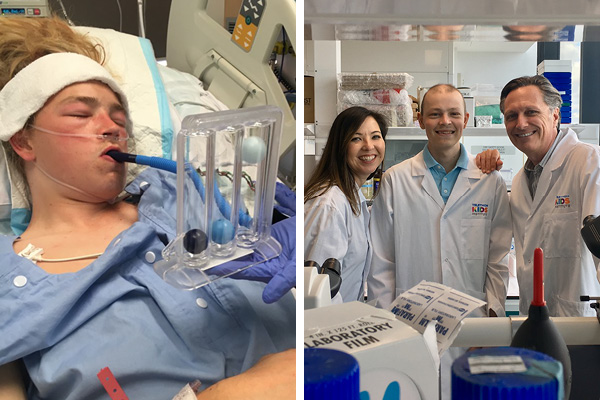
News & Events
Meet Baxter HutchinsonBaxter Hutchinson was diagnosed with two life-threatening brain tumours a year ago, aged 17. Since then he has undergone surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy in his journey to beat the cancer.

News & Events
Three-continent clinical trial aims to improve survival for aggressive kids’ brain cancerThe Kids Research Institute Australia and Perth Children’s Hospital will lead an international clinical trial of a novel drug combination they hope will increase cure rates for one of the most aggressive forms of childhood brain cancer.

News & Events
Childhood cancer research is getting a $1.05 million boost thanks to Australian Lions Childhood Cancer Research FoundationAustralian Lions Childhood Cancer Research Foundation has announced it will provide $1.05 million of funding to The Kids Research Institute Australia.

News & Events
The Kids researchers seek cure for devastating gliomaThe Kids Research Institute Australia’s cancer researchers will use funds raised in the name of a brave three-year-old girl to launch a new assault on the devastating form of childhood cancer which took her life.
