Search
Research
Homology modeling and monoclonal antibody binding of the der f 7 dust mite allergenThe group 7 allergens are important allergenic specificities for mite-sensitive patients and may need to be incorporated into new diagnostic and therapeutic...
Research
Genome-wide association and large-scale follow up identifies 16 new loci influencing lung functionPulmonary function measures reflect respiratory health and are used in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Research
Role of innate immunity in the development of allergy and asthmaThe purpose of this review is to examine the role of innate immunity in the lungs in the development of allergy and asthma.
Research
The hygiene hypothesis revisited: role of materno-fetal interactionsFor 20 years, the hygiene hypothesis has dominated attempts to explain the increasing prevalence of allergic disease. A causal link between maternal innate immu
Research
UV inhibits allergic airways disease in mice by reducing effector CD4 T cellsIn human asthma, and experimental allergic airways disease in mice, antigen-presenting cells and CD4(+) effector cells at the airway mucosa orchestrate, and CD4
Research
Decreased fibronectin production significantly contributes to dysregulated repair of asthmatic epitheliumIn human asthma, and experimental allergic airways disease in mice, antigen-presenting cells and CD4(+) effector cells at the airway mucosa orchestrate, and CD4
Research
Long-term derangement of antigen presenting cell populations in the respiratory tract following Influenza A infectionThis project investigates how different populations of cells within the respiratory tract immune system are altered during a viral infection.
News & Events
WA researchers lead global centre to eliminate childhood asthmaAn ambitious project that could stop children developing asthma is the centrepiece of a new world-class respiratory research centre launched in Perth.
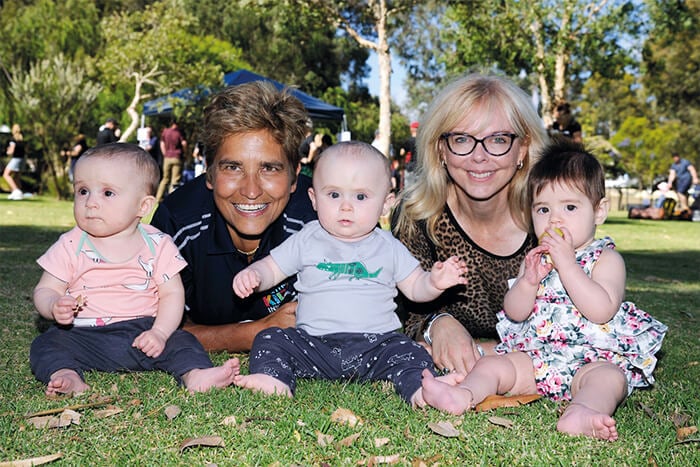

News & Events
ORIGINS Project shines light on Early Childhood DevelopmentA collaboration between The Kids Research Institute Australia and Joondalup Health Campus is poised to be a game-changer for early childhood development.
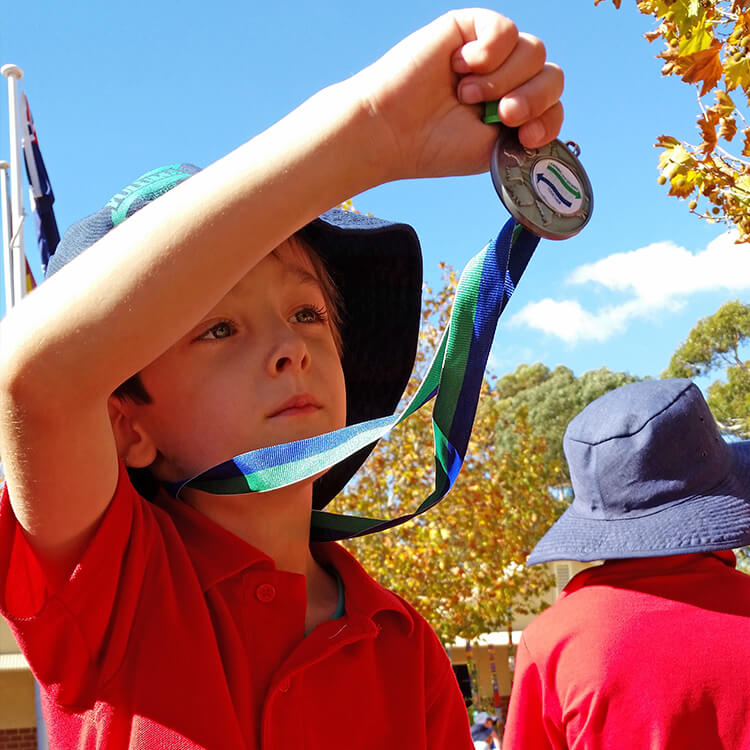

News & Events
New lease on life for DartanyonTwo years on, Michelle and Dartanyon’s health and quality of life have significantly improved. We caught up with Michelle to hear about their journey since we first met them.
